版本新特性
PEP 是什么?
PEP 的全称是 Python Enhancement Proposals,可以翻译为 Python 改进提案。PEP 完全由社区驱动,汇总了多方信息,经过了部分核心开发者 review 和认可,最终形成正式文档,起到了对外公示的作用。
PEP 的官网是:https://www.python.org/dev/peps/,这也就是 PEP 0 的地址。其它 PEP 的地址是将编号拼接在后面,例如:https://www.python.org/dev/peps/pep-0020/ 就是 PEP 20 的链接,以此类推。
官方将 PEP 分成三类:
- I - Informational PEP
- 信息类:这类 PEP 就是提供信息,有告知类信息,也有指导类信息等等。例如 PEP 20(The Zen of Python,即著名的 Python 之禅)、PEP 404 (Python 2.8 Un-release Schedule,即宣告不会有 Python2.8 版本)。
- P - Process PEP
- 流程类:这类 PEP 主要是 Python 本身之外的周边信息。例如 PEP 1(PEP Purpose and Guidelines,即关于 PEP 的指南)、PEP 347(Migrating the Python CVS to Subversion,即关于迁移 Python 代码仓)。
- S - Standards Track PEP
- 标准类:这类 PEP 主要描述了 Python 的新功能和新实践(implementation),是数量最多的提案。例如我之前提到过的 f-string 方式,它出自 PEP 498(Literal String Interpolation,字面字符串插值)。
Python 3.8
海象运算符
Assignment Exppresions,https://peps.python.org/pep-0572/

新增的语法 := 可在表达式内部为变量赋值,帮你少写一行代码
a = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
if (n := len(a)) > 5:
print(f"List is too long ({n} elements, expected <= 5)")
很像 Golang 中的这种写法:
import "fmt"
func main() {
if age := 20; age > 18 {
fmt.Println("已经成年了")
}
}
if (age:= 20) > 18:
print("已经成年了")
在推导式中也可以使用,通常用于减少执行的次数
# old
[abs(m) for m in members if abs(m) > 10]
# new
[abs_m for m in members if (abs_m := abs(m)) > 10]
函数形参语法 /
函数形参语法 / 用来指明某些函数形参必须是位置形参的形式(而非关键字形参的形式)
在下面的例子中,形参 a 和 b 只能是位置形参,c 或 d 可以是位置形参或关键字形参,而 e 或 f 只能是关键字形参:
def f(a, b, /, c, d, *, e, f):
print(a, b, c, d, e, f)
f(10, 20, 30, d=40, e=50, f=60) # ok
f(10, b=20, c=30, d=40, e=50, f=60) # b cannot be a keyword argument
f(10, 20, 30, 40, 50, f=60) # e must be a keyword argument
这个特性更多地被用在标准包中,比如 len()
(function) def len(
__obj: Sized,
/
) -> int
>>> a=[1,2,3]
>>> len(a)
3
>>> len(__obj=a)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
TypeError: len() takes no keyword arguments
f-string 支持 = 语法
形式为 f'{expr=}' 的 f 字符串将扩展表示为表达式文本,加一个等于号,再加表达式的求值结果。
from datetime import date
name = 'Nick'
birthday = date(2001, 6, 4)
print(f'{name=} {birthday=}')
# "user='Nick' birthday=datetime.date(2001, 6, 4)"
可以更细致地控制所要显示的表达式结果
delta = date.today() - birthday
print(f'{delta.days=:,d}')
# 'delta.days=8,164'
Python 3.9
字典的合并和更新
合并 (|) 与更新 (|=) 运算符已被加入内置的 dict 类,扩充了现有的 e 和 {**d1, **d2} 字典合并方法。
字典添加两个新的运算符,'|' 和 '|='。
|用于合并字典,相当于dict.update|=用于更新,相当于{**d1, **d2}
a = {"k1": 1, "k2": 2}
b = {"k3": 3, "k4": 4}
print(a | b)
# {'k1': 1, 'k2': 2, 'k3': 3, 'k4': 4}
a = {"k1": 1, "k2": 2}
b = {"k2": 3, "k3": 4}
a |= b
print(a)
# {'k1': 1, 'k2': 3, 'k3': 4}
list 和 dict 成为通用类型
可以将 list 或 dict 直接作为列表和字典的类型注释,而不必依赖 typing.List 或者 typing.Dict
# old
from typing import Dict, List
def func(l: List[str], d: Dict[str, int]):
pass
# new
def func(l: list[str], d: dict[str, int]):
pass
Python 3.10
类型检查 Union 的更优替代
使用 | 代替 Union
# old:
from typing import Union
def func(value: Union[int, float]) -> Union[int, float]:
return value
# new:
def func(value: int | float) -> int | float:
return value
上下文管理器的优化
with 支持使用外层圆括号来使用多个上下文管理器,可以连续多行地书写
with (
open("somefile.txt") as some_file,
open("otherfile.txt") as other_file,
):
...
模式匹配(Pattern Matching)
类似于 switch/case 的一个语法
# 匹配字符串
def func(day):
match day:
case "Monday":
return "Here we go again..."
case "Friday":
return "Happy Friday!"
case "Saturday" | "Sunday": # Multiple literals can be combined with `|`
return "Yay, weekend!"
case _:
return "Just another day..."
# 匹配元组(拆包)
def match_person(person):
match person:
case (name, 'M', age):
print(f'He is {name}, aged {age}.')
case (name, 'F', age):
print(f'She is {name}, aged {age}.')
case (name,):
print(f'We only know the name is {name}, others are secrets.')
# 匹配对象
from dataclasses import dataclass
@dataclass
class Command:
command: str
arguments: list[str]
def run_command(command: Command):
match command:
case Command(command="load", arguments=[filename]):
print(f"Loading file: {filename}.")
case Command(command="save", arguments=[filename]):
print(f"Saving to file: {filename}.")
case Command(command="quit" | "exit" | "bye", arguments=["--force" | "-f"]):
print("Sending SIGTERM and quitting the program.")
quit()
case Command(command="quit" | "exit" | "bye"):
print("Quitting the program.")
quit()
case _:
print(f"Unknown command: {command!r}.")
Python 3.11
异常说明
在 except 子句中,可以调用 add_note() 在引发错误时传递自定义消息。
import math
try:
math.sqrt(-1)
except ValueError as e:
e.add_note("Negative value passed! Please try again.")
raise
typing.Self
函数的返回值是 self 或类本身的新实例,可以使用 typing.Self
from typing import Self
class SomeClass:
def __init__(self, a, b):
self.a = a
self.b = b
def change_b(self, b) -> Self:
self.b = b
return SomeClass(self.a, self.b)
Python 3.12
Python 3.12 正式版(3.12.0 final)于 2023.10.2 发布,https://docs.python.org/zh-cn/3.12//whatsnew/3.12.html
f - 字符串语法的改进
PEP 701 取消了对 f -string 使用的一些限制:其内部的表达式部分现在可以是任何有效的 Python 表达式
怎么解释呢,最直观的例子就是,f-string 甚至可以自己嵌套自己:
f"{f"{f"{f"{f"{f"{1+1}"}"}"}"}"}"
引号重用
以前,引号不能在 f-string 中重复使用,所以引号的嵌套最多四层
>>> f"""{f'''{f'{f"{1+1}"}'}'''}"""
'2'
而现在,可以使用 " 来嵌套 f 字符串了
>>> f"{f"{f"{f"{f"{f"{1+1}"}"}"}"}"}"
'2'
多行表达式和注释
f"This is the playlist: {", ".join([
'Take me back to Eden', # My, my, those eyes like fire
'Alkaline', # Not acid nor alkaline
'Ascensionism' # Take to the broken skies at last
])}"
# 'This is the playlist: Take me back to Eden, Alkaline, Ascensionism'
反斜框和 unicode 字符
songs = ["That's Life", "Lovin' You", "Johnny B. Goode"]
print(f"This is the playlist: {"\n".join(songs)}")
# This is the playlist: That's Life
# Lovin' You
# Johnny B. Goode
print(f"This is the playlist: {" \N{BLACK HEART SUIT} ".join(songs)}")
# This is the playlist: That's Life ♥ Lovin' You ♥ Johnny B. Goode
类型参数语法和 type 语句
前置:关于泛型
type hints 很早就提供了对泛型的语法支持
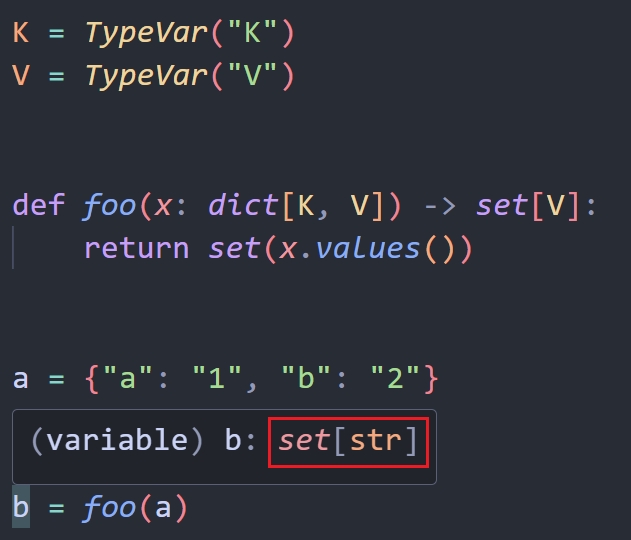
K = TypeVar("K")
V = TypeVar("V")
def foo(x: dict[K, V]) -> set[V]: ...
这个泛型的 type hints 不参与运算, 主要是给类型�检查器 (type checkers) 看的。有了 TypeVar 以后你在 IDE 里面可以看到,推导出来的类型是什么。
简化泛型类和泛型函数
以前,type hints 在定义泛型类和泛型函数时的语法是这样的:
from typing import List, TypeVar, Generic
T = TypeVar("T") # T 需要被声明
class Queue(Generic[T]):
def __init__(self) -> None:
self.items: List[T] = []
def push(self, item: T) -> None:
self.items.append(item)
def pop(self) -> T:
return self.items.pop(0)
在调用时,我们可以通过指定��具体类型,来获得更友好的类型提示
q = Queue[int]()
q.push(1)
q.pop() # 1
q.push("string") # **不会**报错
TypeVar的语法看上去有些累赘。如果你有使用其他语言的经验,就知道在 Java、C#、TypeScript 等语言中,可以直接通过前置<T>来简短地声明泛型,而在 Type Hints 中必须使用TypeVar才能表示泛型。这看起来很奇怪,也有些别扭,但这是不得已而为之,因为 Python 在引入 Type Hints 时不希望更改语言的其他语法。通过元编程技巧,可以巧妙地实现
Sequence[T]这样的语法,但T必须要在其他地方定�义,否则就需要深入修改 Python 的解释器。因此在 Type Hints 中声明泛型需要使用TypeVar构造函数,而在 Java、C#、TypeScript 等语言中则不需要。
而 PEP 695 引入了一种新的、更紧凑、更明确的方式为类和函数定义泛型:
def max[T](args: Iterable[T]) -> T:
...
class list[T]:
def __getitem__(self, index: int, /) -> T:
...
def append(self, element: T) -> None:
...
变化如下:
- 当你写多了
TypeVar之后,你一定会认为这是一个非常累赘的东西。而此 PEP 简化了这个语法。 - 顺便省略了 Generic。
type 语句
以前,声明类型别名(TypeAlias)是这么写的:
Point = tuple[float, float]
这个写法有一些令人费解,因为和普通变量赋值很类似。官方甚至在 3.10 中推荐使用新 TypeAlias 类型来显式表示类型别名,使其更加清晰:
from typing import TypeAlias
Hexadecimal: TypeAlias = str | int
也更加复杂了。。
而 PEP 695 引入了更合适的、声明类型别名的方法:使用 type 语法
type Point = tuple[float, float]
当然支持了新的泛型写法:
type Point[T] = tuple[T, T]
推导式内联
字典、列表和集合推导式现在都是内联的,而不是为每次执行推导式都创建一个新的一次性函数对象。
此改动将推导式的执行速度提高至多两倍。
def f(lst):
return [x for x in lst]
之前,推导式是被编译成嵌套函数执行的,这意味着每次调用 f() 都会生成一个新的、一次性使用的函数对象,用完即扔,如以下字节码所示:
1 0 RESUME 0
2 2 LOAD_CONST 1 (<code object <listcomp> at 0x...)
4 MAKE_FUNCTION 0 // 为列表推导式创建了�一个函数对象
6 LOAD_FAST 0 (lst) // 加载本地变量lst
8 GET_ITER // 创建lst的一个迭代器
10 CALL 0 // 调用
20 RETURN_VALUE
// 以下是列表推导式的内部实现
Disassembly of <code object <listcomp> at 0x...>:
2 0 RESUME 0
2 BUILD_LIST 0 // 创建一个空列表
4 LOAD_FAST 0 (.0) // 加载局部变量(也就是x)
>> 6 FOR_ITER 4 (to 18) // 开始迭代
10 STORE_FAST 1 (x) // 将当前迭代到的值储存在x中
12 LOAD_FAST 1 (x) // 加载x
14 LIST_APPEND 2 // 添加到列表中
16 JUMP_BACKWARD 6 (to 6)
>> 18 END_FOR
20 RETURN_VALUE
根据 PEP 709,f() 的新字节码如下:
1 0 RESUME 0
2 2 LOAD_FAST 0 (lst)
4 GET_ITER
6 LOAD_FAST_AND_CLEAR 1 (x) // 新操作符。这将在运行推导式之前保存外部 x 值到栈上
8 SWAP 2 // 交换栈上的两个值(交换迭代器和x,将迭代器移到操作数栈顶)
10 BUILD_LIST 0 // 创建一个空列表
12 SWAP 2 // 交换栈上的两个值(交换迭代器和空列表,将迭代器移到栈顶)
>> 14 FOR_ITER 4 (to 26) // 迭代
18 STORE_FAST 1 (x)
20 LOAD_FAST 1 (x)
22 LIST_APPEND 2
24 JUMP_BACKWARD 6 (to 14)
>> 26 END_FOR
28 SWAP 2 // 交换栈上的两个值(交换列表和外部x值,将外部x值移到栈顶)
30 STORE_FAST 1 (x) // 加外部 x 的值重新存储
32 RETURN_VALUE
引入了一个新的操作码(optcode)LOAD_FAST_AND_CLEAR 来保存(可能已经存在的)外部 x 值,完成了局部变量和本地变量的隔离。
解释器级的单独 GIL
PEP-684 允许给每个子解释器创建 GIL,使同一个进程下的多个子解释器不再共享同一个 GIL,而是拥有各自独有的 GIL。允许 Python 实现真正的并行处理。
不过此特性目前仅能通过 C-API 使用,相应的 Python API 可能得等到 3.13 了
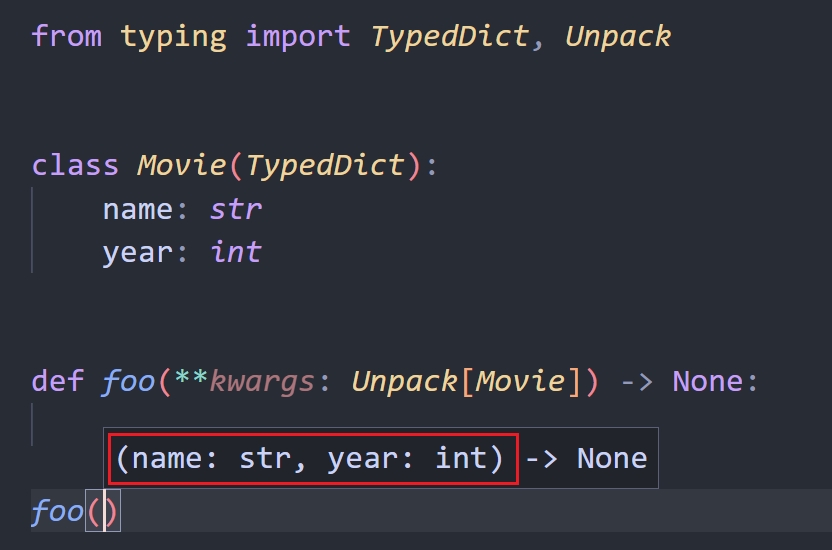
使用 Unpack 和 TypedDict 来标注 **kwargs
**kwargs 是个很灵活的语法,但是你往往在使用 **kwargs 参数的函数中得不到任何有效的类型提示。
现在,使用 Unpack 和 TypedDict 来标注 **kwargs 后,写位置参数的时候就有完整的类型提示了。
from typing import TypedDict, Unpack
class Movie(TypedDict):
name: str
year: int
def foo(**kwargs: Unpack[Movie]) -> None: ...
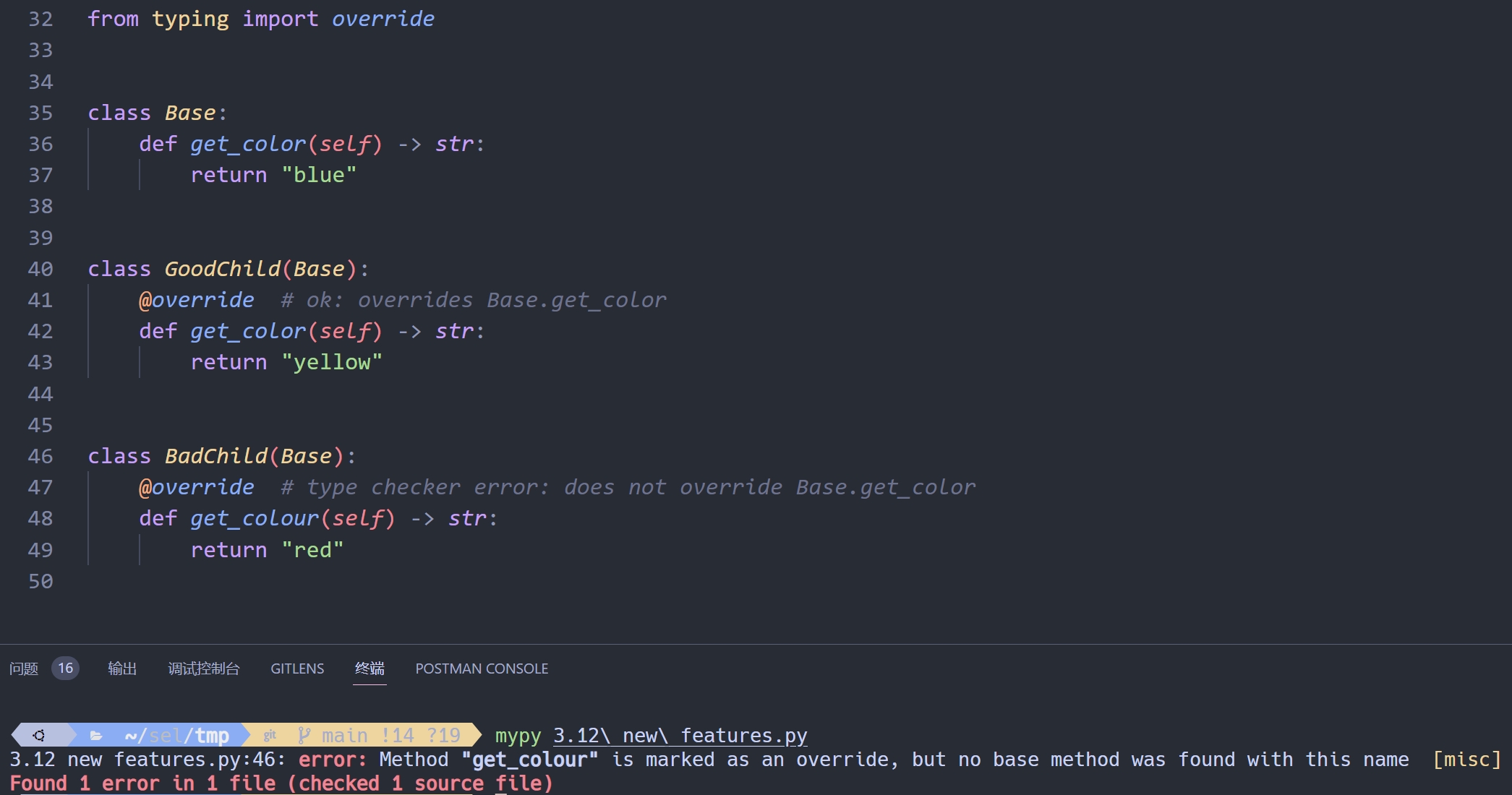
PEP 698,typing.override() 装饰器
override 装饰器可以告诉类型检查器:这个方法需要覆写基类
这允许类型检查器在打算重写基类中的某个方法但实际上没有重写的情况下捕获错误
from typing import override
class Base:
def get_color(self) -> str:
return "blue"
class GoodChild(Base):
@override # ok: overrides Base.get_color
def get_color(self) -> str:
return "yellow"
class BadChild(Base):
@override # type checker error: does not override Base.get_color
def get_colour(self) -> str:
return "red"
Python 3.13
小特性
- 更好的交互式解释器
- 带颜色的提示符。
- 多行编辑并保留历史记录。
- 使用 F1 浏览交互式帮助并带有单独的命令历史。
- 使用 F2 浏览去除了输出以及 >>> 和 ... 提示符的历史。
- 使用 F3 进入“粘贴模式”以更方便地粘贴大段代码(再次按 F3 返回常规提示符)。
- 可以输入 REPL 专属的命令如 help, exit 和 quit 而无需使用在命令名后添加圆括号的调用形式。
Python 3.14
t-string
name = "World"
# f-string 语法
formatted = f"Hello {name}!"
print(type(formatted)) # 输出:<class 'str'>
print(formatted) # 输出:Hello World!
# t-string 语法
templated = t"Hello {name}!"
print(type(templated)) # 输出:<class 'string.templatelib.Template'>
print(templated.strings) # 输出:('Hello ', '')
print(templated.interpolations[0].value) # 输出:World
print("".join(
item if isinstance(item, str) else str(item.value)
for item in templated
)) # 输出:Hello World!
f-string 的缺点
- 注入风险
- 没有提供在字符串组合前拦截和转换插入值的机制
而 t-string 的核心特点是延迟渲染
- 提供了统一的字符串处理机制,可以根据实际需求实现各种自定义渲染逻辑